

Business
How to Buy Solana Safely and Avoid Common Crypto Mistakes
Solana has been one of the hottest topics of discussion [ ]
Technology
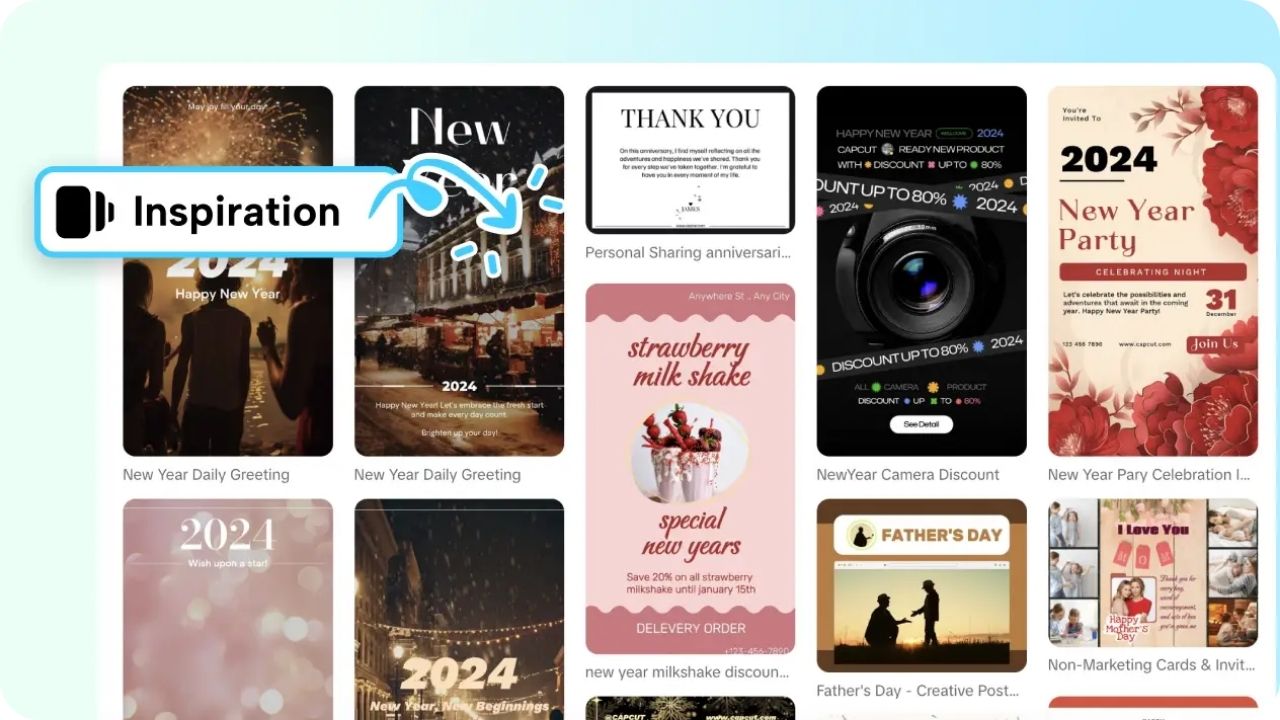
How Pippit Can Make You Celebrate the New Year in a Stylish Way
The New Year is the time to celebrate the birthdays of [ ]

Technology
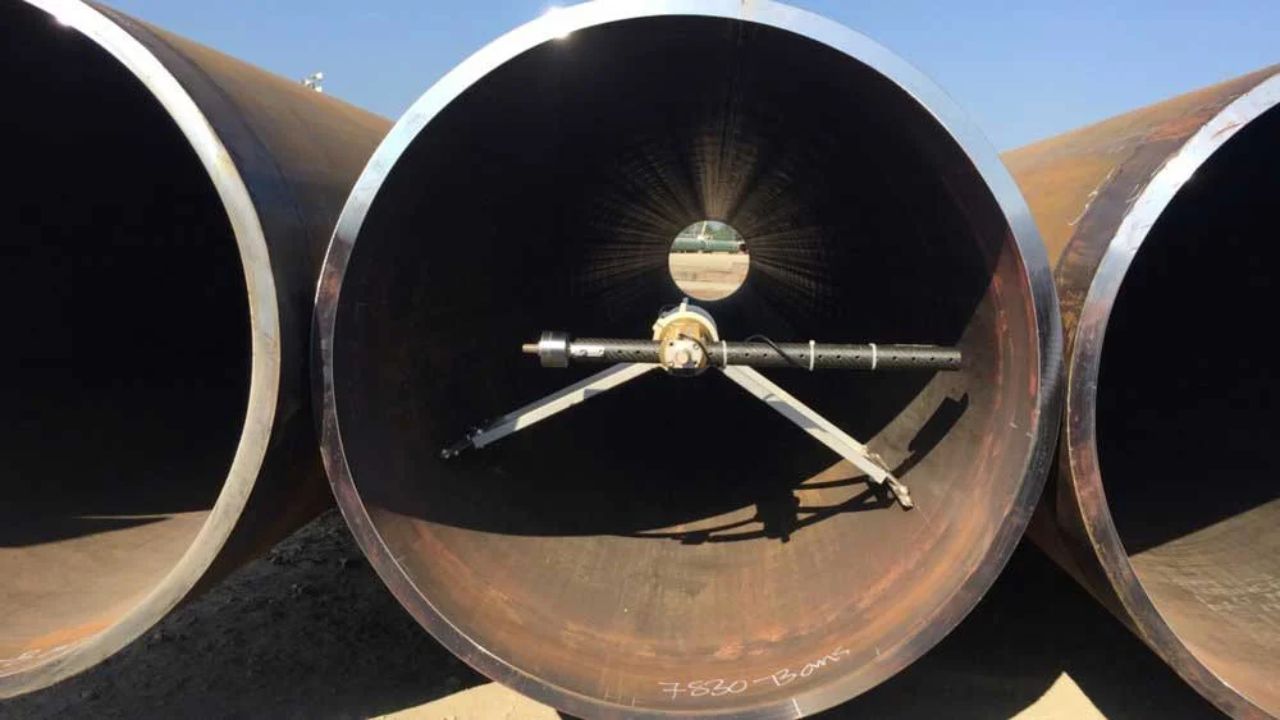
Pipe Measurement Made Simple – TUSPIPE on ND, ID, and OD
When it comes to the steel pipe industry, the accuracy [ ]

Technology
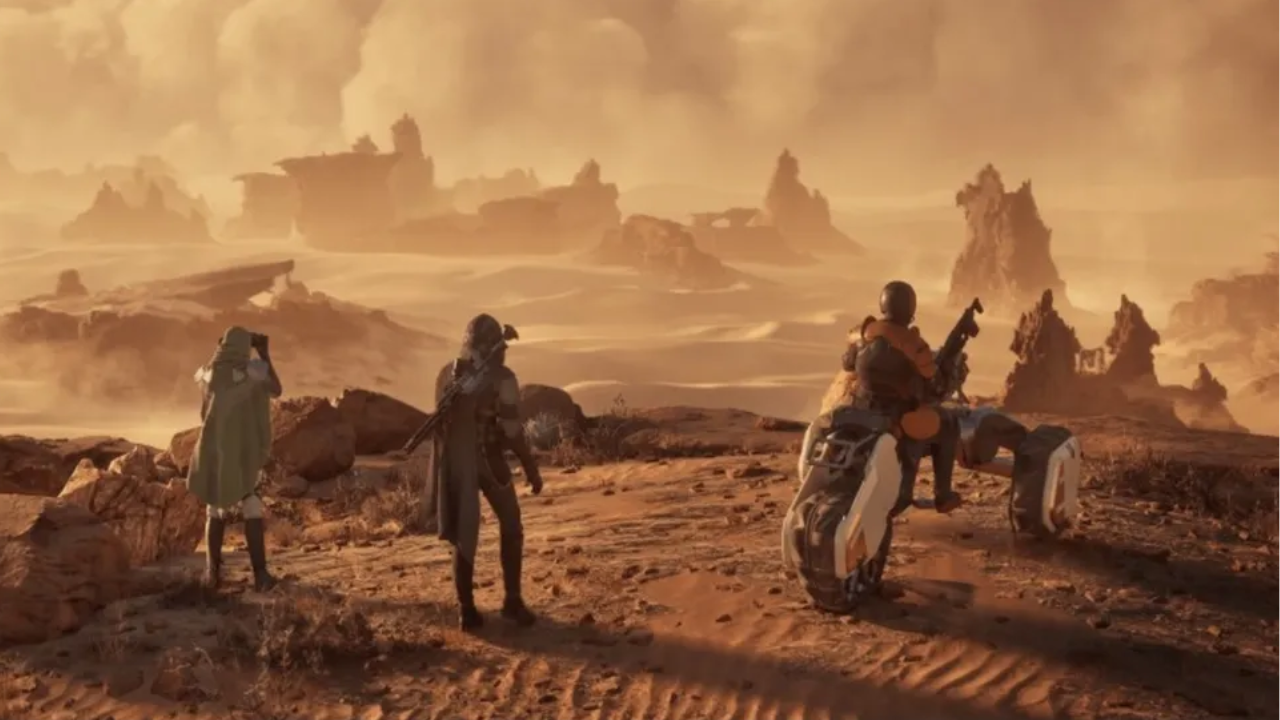
Dune Awakening: How to Buy Solari on U4GM Step-by-Step
In a world where multiplayer survival games are constan [ ]

Technology
How Pippit’s Digital Clothing Models Boost Online Sales
In the current market, online fashion competition deman [ ]

Technology
The Importance of Missing Label Detection in Labeling Machines
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, especially in [ ]

Lifestyle
Bulk Disney Pins: Perfect for Corporate Events & Promotions
Businesses always seek unique and memorable ways to con [ ]
Technology
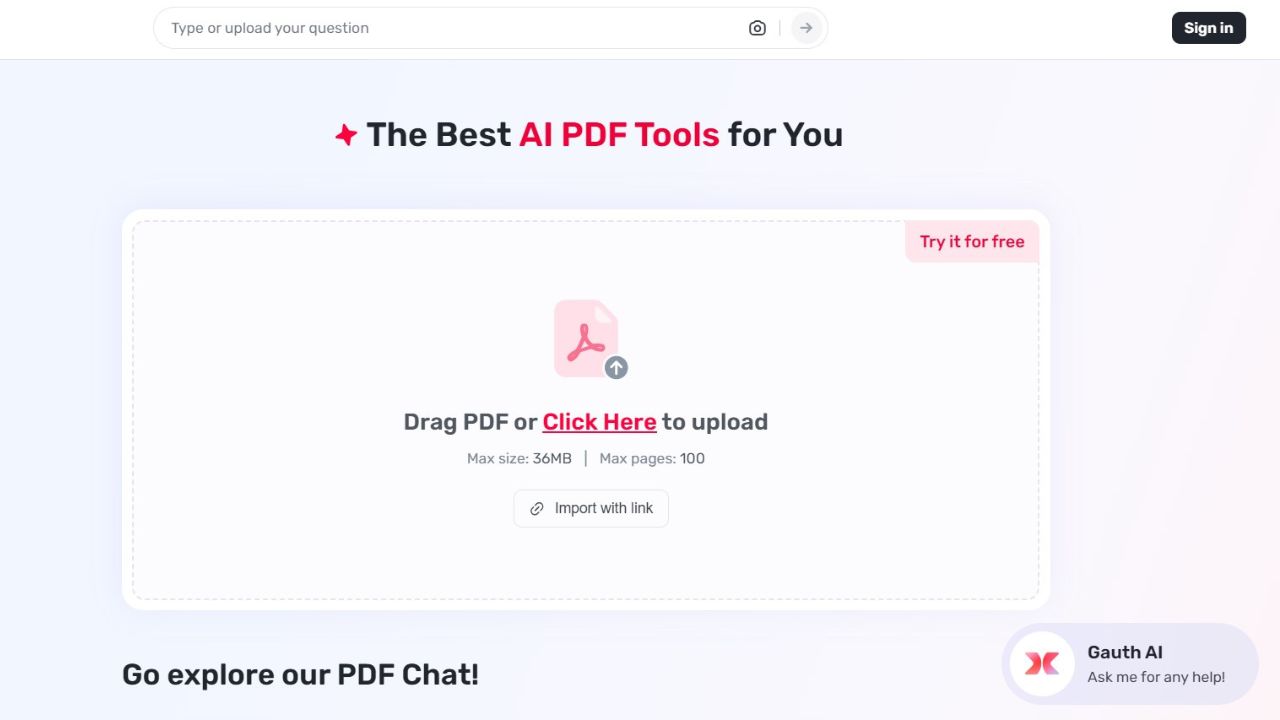
Gauth: Making Research Papers Easier to Digest
Research papers are major tools for raising knowledge a [ ]
Lifestyle
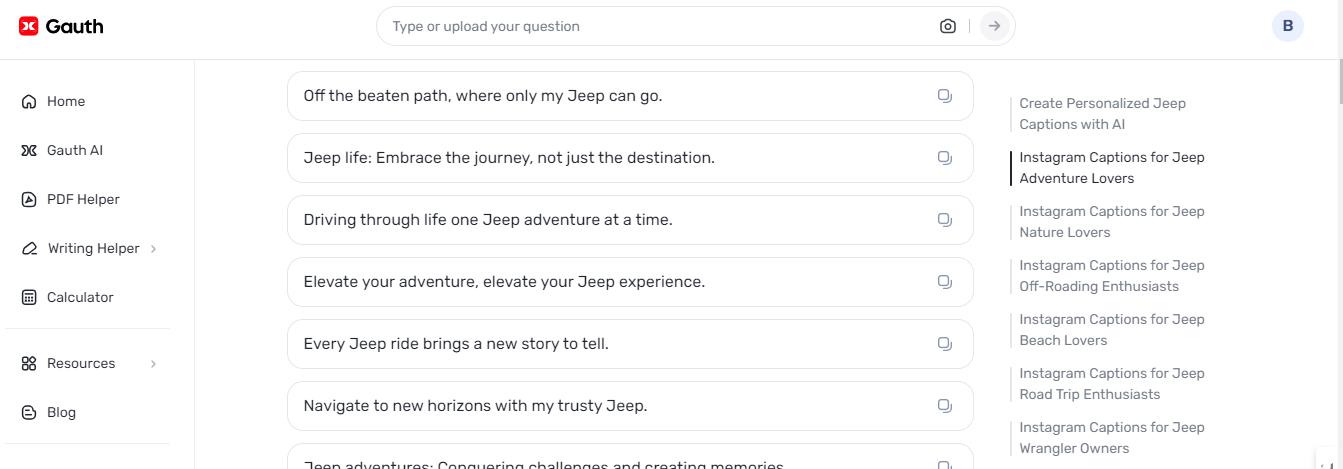
Jeep Captions for Instagram: Elevate Your Adventure with Gauth
In the world of social media, striking descriptions cou [ ]

Business
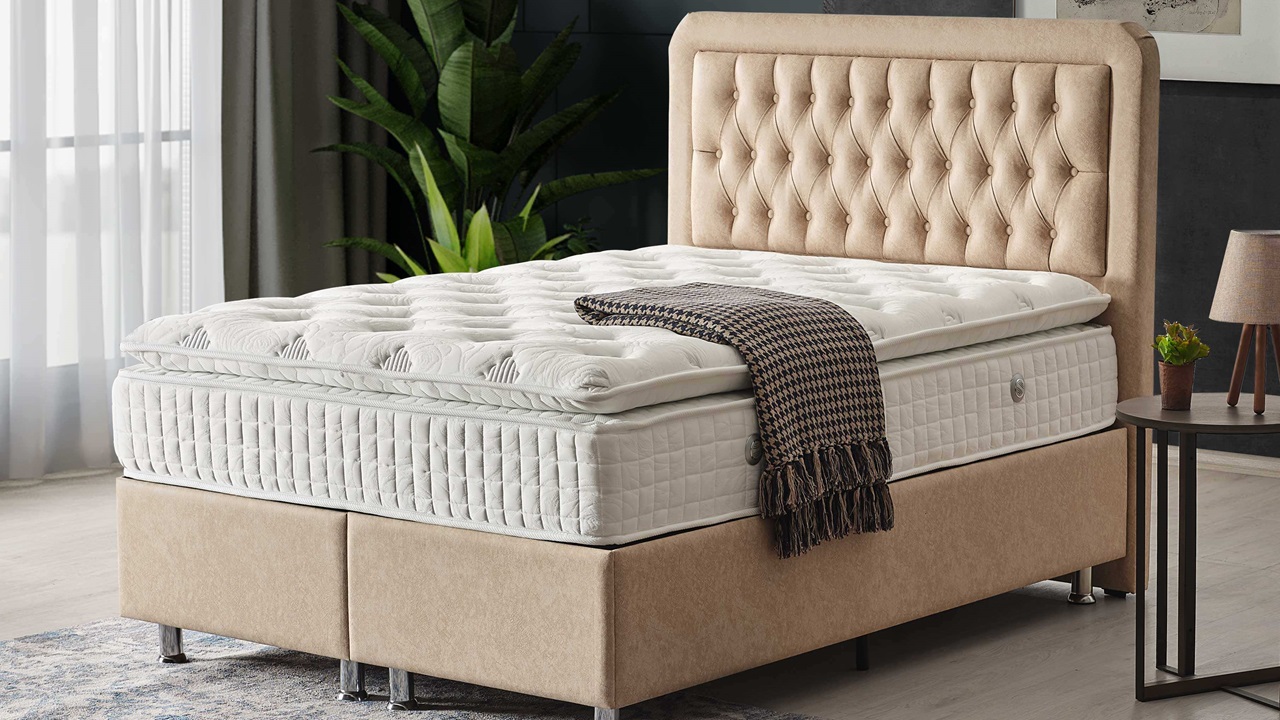
A Complete Beginner’s Guide to Buy Mattress Wholesale
Buying mattresses is one of the most profitable investm [ ]

Lifestyle
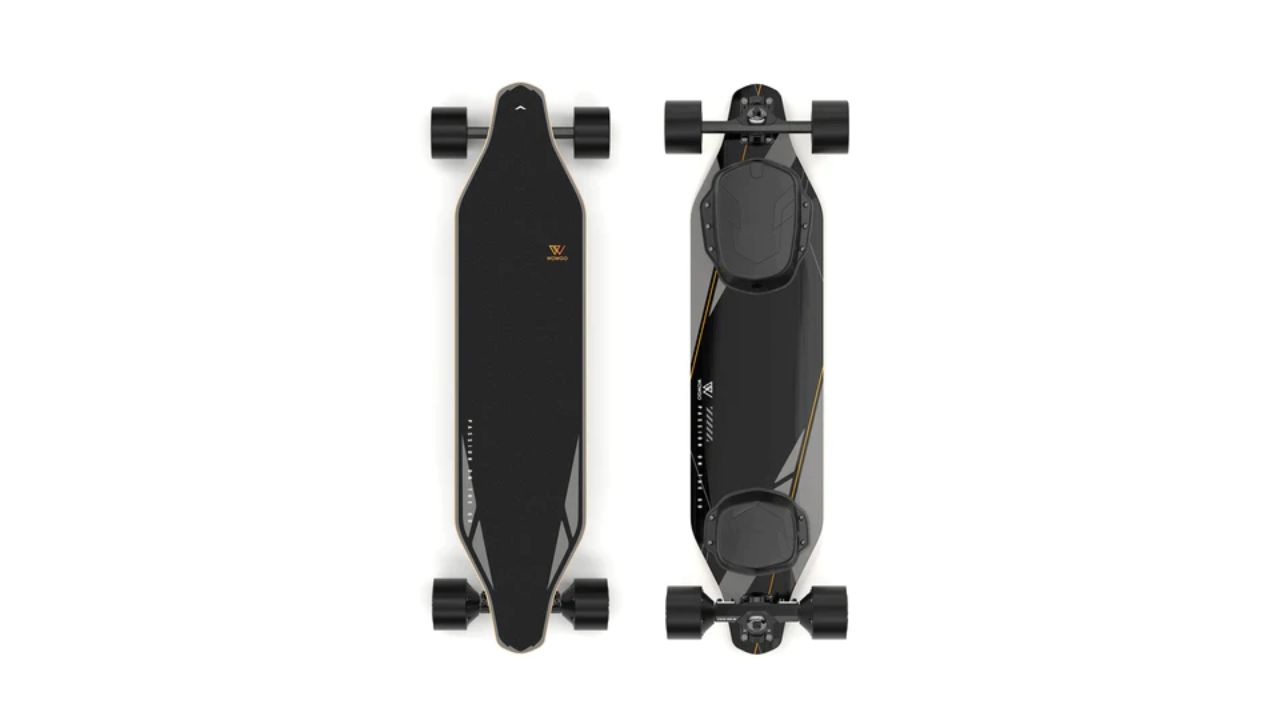
Don’t Miss Out on Riding Thrills and Discounts – Get Your Electric Skateboard Coupon Link
The cost of the skateboard is what prevents many skateb [ ]

Lifestyle
Elevate Your Gaming Experience: Buy FC 24 Coins for PS4 Online
Inside the dynamic world of FIFA 24 ultimate group (FUT [ ]
