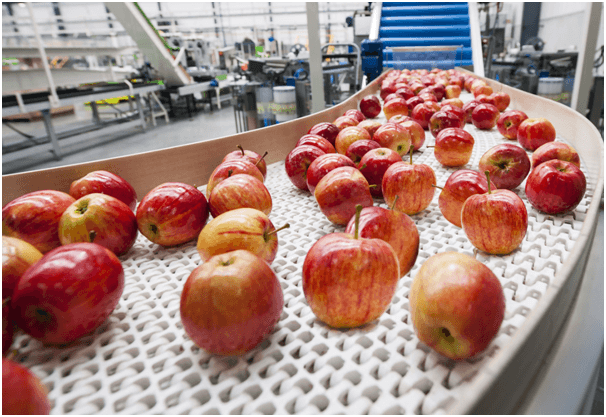
Fruit waxing is gaining the attention of health workers and retailers across the world. The topic has been debatable over the past few years, especially in the medical sector. With that said, coating fruits using wax has become a common practice used in improving post-harvest buyer appeal. As such, the fruit waxing strategy helps in retaining moisture in these fruits while inhibiting the development of molds. Other than that, it’s vital to understand the existing different types of waxes for fruit.
- Natural Wax As A Protective Fruit Coating
Water is the main component of fresh fruits. It constitutes up to 75 percent of the fresh produce. As such, fruits are mainly covered using a layer of natural wax. This acts as a primary barrier that helps in reducing moisture loss while giving the fruit a shiny look. Since the fruit loses its original moisture after the harvest, waxing plays a key role in giving the fruit a naturally-healthy appearance.
- Waxing Materials Used
Different waxing materials can be used in the fruit coating. Some of the wax types can be derived from nature while others may be harvested from insects. Some of these waxes are beeswax and shellac. Others can be derived from plants. They include carnauba wax as well as candelilla wax. With that said, these waxes have been assessed by the WHO Expert Committee in charge of international food safety.
- Manual Rubbing
The process of fruit waxing takes place when the wax is applied on the surface of the fruit using a soft brush or an absorbent cloth. After that, the fruits are dried for about 15 minutes. This is usually a time-consuming process that requires manpower.
- Automated Brushing
This refers to an automated fruit waxing method. The liquefied wax will be dispensed over the brush and then continuously applied over the surface of the fruit to form a thin coating. Fo you to have an even application of wax, the brush should completely be saturated with the wax. Additionally, the wax may be sprayed via a low-pressure nozzle.

- Health Risks Associated With the Consumption Of Waxed Fruits
Food waxing is a preservation technique used in current times. The practice was initially accepted before the associated chemistries were comprehended. The technique is still practiced. However, it has certain health risks appended to it. One perfect example is the use of morpholine as a solvent in the creation of wax coatings, especially in fruits as well as vegetables. When the element gets in contact with nitrate, it forms a toxic chemical that enhances the growth of carcinogens.
- Dipping
The dipping method in the fruit waxing process is applied when the fruits have a coating of paraffin wax. To be successful, the fruits are dipped in the melted paraffin wax for approximately one second. After that, the paraffin solidifies on the surface of the fruit.
- Preventing Associated Health Risks
The utilization of morpholine as an agent in the waxing of fruits is pretty common in the food consumption sector. Even though its presence is negligible, the lump sum accumulation of NMOR is a threat to health. To overcome the issue, wipe and wash your fruits before consuming. You can also scrub the skin using a brush to get rid of the edible wax.
Take-Home Also, if you are too keen on the health hazards of fruit and food waxing, you may peel the skin before eating.